Encyclopedia
PERGAMOS; PERGAMUMpur'-ga-mos, or pur'-ga-mum (he Pergamos, or to Pergamon):
1. History:
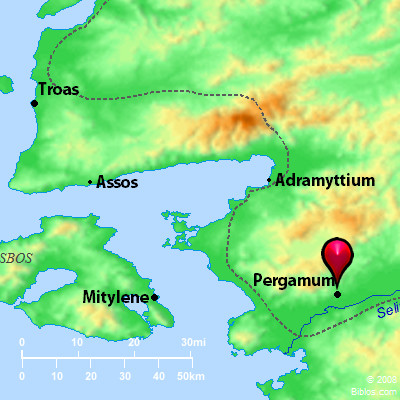
Pergamos, to which the ancient writers also gave the neuter form of the name, was a city of Mysia of the ancient Roman province of Asia, in the Caicus valley, 3 miles from the river, and about 15 miles from the sea. The Caicus was navigable for small native craft. Two of the tributaries of the Caicus were the Selinus and the Kteios. The former of these rivers flowed through the city; the latter ran along its walls. On the hill between these two streams the first city stood, and there also stood the acropolis, the chief temples, and theaters of the later city. The early people of the town were descendants of Greek colonists, and as early as 420 B.C. they struck coins of their own. Lysimachus, who possessed the town, deposited there 9,000 talents of gold. Upon his death, Philetaerus (283-263 B.C.) used this wealth to found the independent Greek dynasty of the Attalid kings. The first of this dynasty to bear the title of king was Attalus I (241-197 B.C.), a nephew of Philetaerus, and not only did he adorn the city with beautiful buildings until it became the most wonderful city of the East, but he added to his kingdom the countries of Mysia, Lydia, Caria, Pamphylia and Phrygia. Eumenes II (197-159 B.C.) was the most illustrious king of the dynasty, and during his reign the city reached its greatest height. Art and literature were encouraged, and in the city was a library of 200,000 volumes which later Antony gave to Cleopatra. The books were of parchment which was here first used; hence, the word "parchment," which is derived from the name of the town Pergamos. Of the structures which adorned the city, the most renowned was the altar of Zeus, which was 40 ft. in height, and also one of the wonders of the ancient world. When in 133 B.C. Attalus III, the last king of the dynasty, died, he gave his kingdom to the Roman government. His son, Aristonicus, however, attempted to seize it for himself, but in 129 he was defeated, and the Roman province of Asia was formed, and Pergamos was made its capital. The term Asia, as here employed, should not be confused with the continent of Asia, nor with Asia Minor. It applied simply to that part of Asia Minor which was then in the possession of the Romans, and formed into the province of which Pergamos was the capital. Upon the establishment of the province of Asia there began a new series of coins struck at Pergamos, which continued into the 3rd century A.D. The magnificence of the city continued.
2. Religions:
There were beautiful temples to the four great gods Zeus, Dionysus, Athena and Asklepios. To the temple of the latter, invalids from all parts of Asia flocked, and there, while they were sleeping in the court, the god revealed to the priests and physicians by means of dreams the remedies which were necessary to heal their maladies. Thus opportunities of deception were numerous. There was a school of medicine in connection with the temple. Pergamos was chiefly a religious center of the province. A title which it bore was "Thrice Neokoros," meaning that in the city 3 temples had been built to the Roman emperors, in which the emperors were worshipped as gods. Smyrna, a rival city, was a commercial center, and as it increased in wealth, it gradually became the political center. Later, when it became the capital, Pergamos remained the religious center. As in many of the towns of Asia Minor, there were at Pergamos many Jews, and in 130 B.C. the people of the city passed a decree in their favor. Many of the Jews were more or less assimilated with the Greeks, even to the extent of bearing Greek names.
3. Christianity:
Christianity reached Pergamos early, for there one of the Seven Churches of the Book of Re stood, and there, according to Revelation 2:13, Antipas was marryred; he was the first Christian to be put to death by the Roman state. The same passage speaks of Pergamos as the place "where Satan's throne is," probably referring to the temples in which the Roman emperors were worshipped. During the Byzantine times Pergamos still continued as a religious center, for there a bishop lived. However, the town fell into the hands of the Seljuks in 1304, and in 1336 it was taken by Suleiman, the son of Orkhan, and became Turkish.
The modern name of the town, which is of considerable size, possessing 15 mosques, is Bergama, the Turkish corruption of the ancient name. One of its mosques is the early Byzantine church of Sophia. The modern town is built among the ruins of the ancient city, but is far less in extent. From 1879 to 1886 excavations among the ruins were conducted by Herr Humann at the expense of the German government. Among them are still to be seen the base of the altar of Zeus, the friezes of which are now in the Pergamon Museum, Berlin; theater, the agora, the gymnasium and several temples. In ancient times the city was noted for its ointments, pottery and parchment; at present the chief articles of trade are cotton, wool, opium, valonia, and leather.
E. J. Banks
PER'GAMOS, a city of Mysia, 20 ms. from the Mediterranean, now Bergama, pop. about 25,000. It was celebrated for its library of 25,000 rolls. It is 50 ms, n. from Smyrna and contains many interesting ruins.
Strong's Greek
G4010: PergamosPergamum, a city of Mysia